In today’s fast-moving world, handling your money well is more important than ever. There are lots of ways to invest and save money out there, which can be overwhelming. But if you understand some basic rules about managing money wisely, it can help you stay financially stable and even grow your wealth.
In this article, We will talks about some simple rules that act like guides for people dealing with money matters. For instance, there’s a rule called “The Net Worth Rule” that helps you figure out how well you’re doing financially based on your age and how much you earn. Then there’s the “10% Growth Rule,” which suggests increasing your investments as your income goes up. These rules give you a clear plan for managing your money. Each rule, like the “Rule of 72” for understanding how investments grow or the “100-age rule” for deciding where to put your money, is meant to make money decisions easier and encourage smart habits like saving, investing, and spending wisely.
It’s important to remember that everyone’s financial situation is different, so while these rules are helpful, they should be adjusted to fit your own needs and goals. Let’s explore these principles together to help you make smart choices with your money and build a stable and prosperous future.
we will discuss just 10 simple rules to take control of your finances
Let’s understand each of these rules in detail.
You may also Read:
- Magic of the 8-4-3 Rule in Mutual Fund Investing
- 7 Risk Management Techniques in Breakout and Retest Trading
- Mastering Breakout and retest trading strategy
10 simple personal finance Rule
10 Easy Rules to Master Your Personal Finance Journey are Following
- THE NET WORTH RULE
- RULE OF 72
- RULE OF 70
- 100-AGE RULE
- 50-30-20 RULE
- 6X RULE
- 20X TERM INSURANCE
- 40% EMI RULE
- 25X RETIREMENT RULE
- THE 10% HIKE RULE

1. ” THE NET WORTH RULE ” for Personal Finance
The Net Worth Rule is a guideline to help you assess your wealth based on your age, income, and net worth. It’s a simple formula that originated from the book “The Millionaire Next Door“ and has variations tailored to different countries, including the United States and India.
Here’s how it works:
- Calculate Your Net Worth: Your net worth is the total value of all your assets (things you own, like savings, investments, property) minus your liabilities (debts, loans, mortgages).
- Determine Your Target Net Worth: Multiply your age by your pre-tax annual income, then divide the result by either 10 or 20, depending on which version of the rule you’re using. In the US version, you divide by 10, and in the Indian version, you divide by 20.
- Compare Your Net Worth: Compare your actual net worth to the target net worth you calculated. If your net worth is higher than the target, you are considered wealthy according to this rule.
For example, let’s say you’re 30 years old and earn Rs 12 lakh annually (before taxes).
In the US version:
- Age: 30
- Pre-tax annual income: Rs 12 lakh
- Calculation: (30 * Rs 12 lakh) / 10 = Rs 36 lakh
According to the US version of the rule, if your net worth is greater than Rs 36 lakh, you are considered wealthy.
In the Indian version:
- Age: 30
- Pre-tax annual income: Rs 12 lakh
- Calculation: (30 * Rs 12 lakh) / 20 = Rs 18 lakh
According to the Indian version of the rule, if your net worth is greater than Rs 18 lakh, you are considered wealthy.
This rule provides a rough benchmark to gauge your financial progress and whether you are accumulating wealth relative to your age and income. However, it’s essential to remember that individual circumstances vary, and other factors, such as cost of living, debt levels, and financial goals, should also be considered when assessing your financial health.

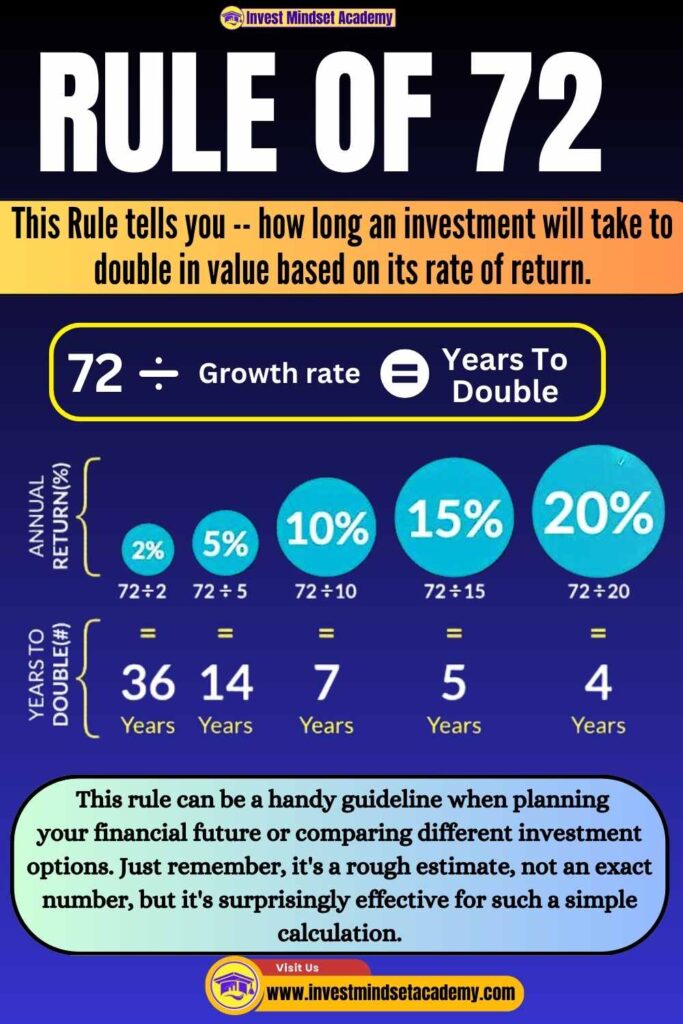
2. RULE OF 72
The Rule of 72 is a quick and easy way to estimate how long it will take for an investment to double in value based on its rate of return. Here’s how it works:
Understand the Rule:
The Rule of 72 is a simple mathematical formula used to estimate the time it takes for an investment to double. It’s based on the principle of exponential growth, where an investment grows at a constant rate over time.
Divide 72 by the Rate of Return:
To use the Rule of 72, you divide the number 72 by the annual rate of return (in percentage) that your investment is expected to earn. The result will be the approximate number of years it will take for your investment to double in value.
Example with a 9% Return: If your investment grows at a rate of 9% per year, you would calculate how long it takes to double like this:
- Divide 72 by 9 (the rate of return).
- 72 / 9 = 8.
So, with a 9% return, it would take approximately 8 years for your investment to double.
Why It’s Useful: The Rule of 72 is a quick, easy tool you can use to get a rough idea of how investments grow over time. It helps you understand the power of compound interest without needing to dive into complex calculations. This rule can be a handy guideline when planning your financial future or comparing different investment options. Just remember, it’s a rough estimate, not an exact number, but it’s surprisingly effective for such a simple calculation.
3. RULE OF 70
The “Rule of 70” is a quick and easy way to understand how fast the value of money decreases because of inflation. Inflation means that over time, the general price of goods and services goes up, which can make your money worth less because you can buy less with the same amount of money.
How Do You Use this rule?
You take the number 70 and divide it by the current inflation rate (the rate at which prices are rising).
For example, if the inflation rate is 7%, you would calculate it like this:
- 70 divided by 7 equals 10.
This means, if inflation stays at 7% per year, the value of your money will be half of what it is today in 10 years. So, if you have Rs1,00000 now, in 10 years, it would only buy what Rs50,000 buys today.

Understanding the Rule of 70 can help you make smarter decisions about saving and investing your money. Knowing that inflation can reduce the value of your money over time, you might decide to invest in ways that could earn more than the inflation rate, so your money doesn’t lose its purchasing power.
So, the Rule of 70 is a handy tool to remind you that inflation can affect how much your money is worth in the future, helping you plan better for your financial needs.
4. 100-AGE RULE
The “100-Age Rule” is a guideline used in personal finance to help individuals decide how to allocate their investment portfolio between equities (stocks) and fixed-income investments (debt). It’s a rule of thumb that aims to balance the risk and return in an investment portfolio based on an individual’s age.
- Equities (Stocks) are considered riskier but offer higher potential returns over the long term. They’re suitable for investors with a longer time horizon who can ride out the volatility in the stock market.
- Debt (Fixed-Income Investments) includes things like bonds and treasury securities. They’re generally safer than equities but offer lower returns. They provide income and stability, making them more suitable for investors who are closer to retirement and need to preserve capital.
Here’s a deeper dive into this rule, its implications, and its limitations:
How It Works
The core idea behind the 100-Age Rule is relatively straightforward. You subtract your current age from 100, and the resulting number represents the percentage of your investment portfolio that you should allocate to equities, with the remainder going into debt investments. The rationale is that younger investors have a longer time horizon before retirement and can therefore tolerate more risk, while older investors should take on less risk as they get closer to needing their investments for retirement.
Example:
If you are 30 years old, according to the 100-Age Rule, you should allocate 70% (100 – 30) of your investment portfolio to equities and the remaining 30% to debt.
Limitations and Considerations
- Not One-Size-Fits-All: The 100-Age Rule is a simplified approach and does not consider individual risk tolerance, financial goals, or life circumstances. Some investors might be more risk-averse or risk-tolerant than their age suggests.
- Changing Lifespans and Retirement Ages: People are living longer, and retirement ages are increasing. Some financial advisors suggest modifying the rule to 110 or 120 minus age to adjust for longer investment horizons.
- Portfolio Diversification: The rule primarily focuses on equities and debt but doesn’t account for other asset classes like real estate, commodities, or alternative investments that can provide additional diversification benefits.
- Adjusting Over Time: As you age, your financial situation, goals, and risk tolerance can change. It’s essential to regularly review and adjust your investment portfolio to reflect these changes, rather than relying solely on a formula.
Adding Gold and Other Assets
Incorporating assets like gold or real estate into your portfolio can help further diversify your investments and potentially reduce overall portfolio risk. Gold, for example, often has a low correlation with stocks and bonds and can act as a hedge against inflation or economic uncertainty.
While the 100-Age Rule provides a simple starting point for asset allocation, it’s crucial to remember that it’s a guideline rather than a strict rule. Individual investors should consider their financial situation, goals, risk tolerance, and investment horizon when deciding on their asset mix. Consulting with a financial advisor can also provide personalized advice tailored to an individual’s unique circumstances.
.
5. 50-30-20 RULE
The 50-30-20 rule is a simple guideline for budgeting your income effectively. It suggests allocating your income into three categories: needs, desires, and investments. Here’s a detailed explanation of each component:
50% for Needs: This category includes essential expenses that are necessary for your basic living requirements. These expenses typically include:
30% for Desires: This category covers discretionary spending on wants and lifestyle choices that enhance your quality of life but are not essential for survival. Examples of expenses in this category include:
20% for Investments: This category focuses on building wealth and securing your financial future through savings and investments. This portion of your income should be allocated towards:
The 50-30-20 rule provides a straightforward framework for budgeting and managing your finances effectively. However, it’s essential to remember that personal finance is not one-size-fits-all, and individual circumstances may vary. You can adjust the percentages based on your specific financial goals, lifestyle preferences, and income level. The key is to find a balance that works for you while ensuring that you prioritize both your short-term needs and long-term financial well-being.
6. 6X RULE
The “6X Rule” is a guideline in personal finance that advises individuals to set aside an emergency fund equivalent to six times their monthly expenses. This rule serves as a practical approach to building a financial safety net that can help you manage unexpected financial emergencies without resorting to high-interest debt or dipping into long-term savings or investments.
Here’s a detailed explanation of how the rule works:
Understanding the 6X Rule
- Basis of the Rule: The rule is based on the principle that having six months’ worth of expenses in savings offers a solid cushion that can help you navigate through financial uncertainties without severely impacting your long-term financial plans.
- Calculation: To apply this rule, first calculate your average monthly expenses, including rent or mortgage payments, utilities, groceries, transportation, insurance, and any other regular payments. Then, multiply this figure by six. The result is the amount you should aim to have in your emergency fund.
- For example, if your monthly expenses amount to Rs 40,000, according to the 6X Rule, you should aim to save: R40,000×6=Rs2,40,000.
Importance of the 6X Rule
- Provides Financial Security: Having a safety net of six months’ expenses gives you peace of mind knowing you can cover unexpected financial shocks without immediately facing financial distress.
- Prevents Debt: In times of emergency, people often resort to using credit cards or taking out loans, leading to high-interest debt. An emergency fund prevents this by providing the necessary funds without borrowing.
- Protects Your Investments: Without an emergency fund, you might be forced to liquidate your investments, possibly at a loss or at an inopportune time, to cover unexpected expenses. The 6X Rule safeguards your investments by providing an alternative source of funds.
- Encourages Discipline: Building up an emergency fund requires financial discipline and planning. It encourages you to manage your expenses and save regularly, which are valuable habits for long-term financial health.
How to Implement the 6X Rule
- Start Small: If saving six months’ worth of expenses seems daunting, start with a smaller goal, such as one month, and gradually increase your savings as your financial situation improves.
- Review and Adjust: Your expenses may change over time due to lifestyle changes, inflation, or changes in your family situation. Regularly review and adjust your emergency fund to ensure it remains relevant to your current monthly expenses.
- Keep It Accessible: Your emergency fund should be easily accessible without significant penalties or delays. Consider keeping it in a savings account or a liquid mutual fund, where you can withdraw the funds quickly when needed.
- Automate Savings: Set up automatic transfers from your checking account to your emergency fund to make the saving process effortless and consistent.
By following the 6X Rule and diligently saving for emergencies, you can establish a solid financial foundation and gain peace of mind knowing that you’re prepared to handle unexpected financial challenges that may arise.
So, the “6X Rule” is a fundamental part of a sound personal finance strategy, providing a strong foundation upon which you can build your financial future.
7. 20X TERM INSURANCE
The “20X Term Insurance” rule suggests that the amount of life insurance coverage you purchase should be at least twenty times your annual earnings. This rule is based on the premise that the life insurance payout should be substantial enough to provide financial security to your dependents in case of your untimely death.
Let’s break down the concept using an example:
Suppose your annual income is Rs 5 lakhs. According to the 20X Term Insurance rule, you would need a term life insurance cover of 20 times your annual income, which would be:
20 * Rs 5 lakhs = Rs 1 crore
Therefore, according to this rule, you should aim to get a term life insurance policy with a coverage amount of Rs 1 crore.
Here’s why this rule can be beneficial:
- Financial Security for Dependents: The primary purpose of life insurance is to provide financial protection to your dependents in the event of your death. By ensuring that your life insurance coverage is sufficient (in this case, 20 times your annual income), you can help maintain your family’s standard of living and cover essential expenses such as mortgage payments, education costs, and daily living expenses.
- Income Replacement: The life insurance payout can serve as a replacement for your lost income, helping your family members maintain their financial stability and meet their ongoing financial needs. With a coverage amount of 20 times your annual income, your dependents would have a substantial sum to rely on for their financial well-being.
- Accounting for Inflation and Future Expenses: By opting for a coverage amount that is significantly higher than your current annual income, you account for factors like inflation and potential future expenses. Over time, the cost of living may increase, and your family’s financial needs may grow. Having a larger life insurance coverage ensures that your loved ones are adequately protected against these potential financial challenges.
- Flexibility and Customization: While the 20X Term Insurance rule provides a general guideline for determining the appropriate coverage amount, it’s essential to assess your specific financial situation and individual needs. Factors such as existing debts, future financial goals, number of dependents, and lifestyle expenses should also be taken into account when selecting the right amount of life insurance coverage.
It’s worth noting that the 20X Term Insurance rule is a rule of thumb and may not be suitable for everyone. Depending on your unique circumstances, you may need more or less coverage. Consulting with a financial advisor can help you determine the optimal amount of life insurance coverage based on your individual financial goals and objectives.
8. 40% EMI RULE
The “40% EMI Rule” is a guideline commonly used in personal finance to help individuals manage their debt responsibly and maintain a healthy balance between loan obligations and other financial priorities. This rule suggests that the total Equated Monthly Installments (EMIs) for all loans should not exceed 40% of your monthly income.
The core idea behind the “40% EMI Rule” is to maintain a healthy balance between your debt obligations and your income. By ensuring that your EMIs do not exceed 40% of your monthly income, you leave enough room for other essential financial activities, such as savings, investments, and covering daily living expenses.
Calculation of 40% EMI RULE
To apply the “40% EMI Rule”, you first need to know your monthly income. Once you have this figure, calculate 40% of it. The total of all your EMIs (for example, home loan, car loan, personal loan, etc.) should not exceed this amount.
Example
Suppose your monthly income is Rs50,000. According to the “40% EMI Rule”, the total of your EMIs should not exceed Rs20,000 (which is 40% of Rs50,000).
The Logic behind 40% rule
- Affordability: Keeping your EMIs within 40% of your income ensures that loans remain affordable. This allows for sufficient financial breathing room to cover other essential expenses, such as rent, utilities, groceries, and education.
- Financial Stability: This rule aims to prevent financial over-leverage, where too much of your income is tied up in debt repayments, leaving little for savings or emergencies. It helps maintain a balance between debt repayment and other financial priorities.
- Investment Opportunities: Adhering to this rule can ensure you have enough disposable income to invest in opportunities that can grow your wealth over time. Over-leveraging with debt might prevent you from making such investments.
- Credit Score: Managing your EMIs effectively and keeping them within a reasonable portion of your income can positively impact your credit score. A lower debt-to-income ratio is viewed favorably by credit bureaus.
Benefits of 40% EMI RULE
- Avoids Over-leveraging: By keeping EMIs within 40% of income, you avoid taking on more debt than you can comfortably handle, reducing the risk of default.
- Financial Stability: It ensures that a significant portion of your income is not tied up in debt repayments, helping maintain financial stability.
- Savings and Investments: With 60% of your income not going towards debt repayment, there’s more scope for savings and investments, which are crucial for long-term financial health and wealth creation.
- Lifestyle Maintenance: Ensuring that your EMIs are manageable helps in maintaining a reasonable standard of living without having to cut back excessively to service debt.
Drawbacks of 40% EMI RULE
- One Size Does Not Fit All: The “40% EMI Rule” is a general guideline and may not be suitable for everyone. Some individuals may have higher financial resilience and can afford to allocate a higher percentage towards EMIs, while for others, even 40% might be too high.
- Does Not Account for Other Obligations: This rule focuses solely on EMIs and does not take into account other financial obligations such as rent, utilities, and insurance, which can also impact your ability to manage debt.
While the “40% EMI Rule” is a helpful guideline for managing debt, it’s important to consider your unique financial situation and obligations. It’s a tool to ensure you don’t overburden yourself with debt but should be adapted to fit your individual circumstances and financial goals. Balancing debt repayment with savings and investments is crucial for achieving financial freedom and stability.
9. 25X RETIREMENT RULE
The “25X Retirement Rule” is a guideline used in financial planning to help individuals determine how much money they need to save for retirement. The rule suggests that you should aim to have at least 25 times your annual expenses saved up by the time you retire. This rule is grounded in the concept of ensuring that your retirement savings are sufficient to support your lifestyle for many years after you stop working, typically assuming a retirement period of 30 years or more.
How It Works
To apply the 25X Retirement Rule, you first need to have a clear understanding of your annual expenses. This includes all costs associated with your lifestyle, such as housing, food, healthcare, transportation, and entertainment. Once you have this number, you multiply it by 25 to calculate your retirement corpus goal.
Example: If your annual expenses amount to Rs 12 lakhs, according to the 25X Retirement Rule, you should aim for a retirement corpus of: 12 lakhs×25=300 lakhs or Rs3.6 crores
Logic Behind the Rule
The Logic for the 25X Retirement Rule stems from the “4% Rule,” which is a widely accepted guideline suggesting that retirees can withdraw 4% of their retirement portfolio annually (adjusted for inflation each year) with a low risk of running out of money over a 30-year retirement period. Essentially, if you have 25 times your annual expenses saved, withdrawing 4% of this amount each year should theoretically allow your retirement savings to last at least 30 years.
Adjustments for Early Retirement
If you plan to retire early, you may need to save more than the standard 25 times your annual expenses. This is because:
- Longer Retirement Period: Early retirees have a longer retirement period to fund, increasing the risk of depleting their retirement savings too early.
- Healthcare Costs: Early retirees may need to account for additional healthcare expenses before they become eligible for government-supported healthcare benefits.
- Lower Social Security Benefits: Early retirement might result in lower social security benefits, as these are often calculated based on your working years and income.
Therefore, aiming for a higher multiple, such as 30X or 35X your annual expenses, can provide a safer cushion and help ensure that your savings are sufficient to support a longer retirement period comfortably.
Important Considerations
While the 25X Retirement Rule provides a straightforward framework for retirement planning, it’s important to consider personal factors and market conditions that could affect your retirement needs:
- Inflation: The value of money decreases over time due to inflation, so it’s important to factor this into your calculations.
- Investment Returns: The rule assumes a certain average annual return on your investments. Higher or lower returns can significantly impact the longevity of your retirement savings.
- Lifestyle Changes: Your expenses in retirement may be significantly different from your current expenses, requiring adjustments to your savings goal.
the 25X Retirement Rule offers a useful starting point for retirement planning, but individual circumstances and goals should guide your exact savings targets. Consulting with a financial advisor can also provide personalized advice tailored to your specific situation.
10. THE 10% HIKE RULE
The “10% Hike Rule” is a strategy for increasing your investment contributions over time, particularly through a Systematic Investment Plan (SIP) in mutual funds. This approach takes into account the potential for your income to grow over the years. By periodically increasing your SIP contribution, you not only adapt your investment to match your increased earning capacity but also significantly boost the potential returns on your investment.
Here’s a detailed explanation of how it works and its impact:
Understanding SIP
A SIP is a method of investing in mutual funds where you contribute a fixed amount regularly, say monthly or quarterly, instead of a lump sum. This strategy benefits from dollar-cost averaging, reducing the risk of investing a large amount at the wrong time.
The Concept of the 10% Hike Rule
The 10% Hike Rule suggests increasing your SIP contribution by 10% every year. This is based on the assumption that your income will likely grow over time due to salary hikes, business growth, or other income sources. Even if your income increases more or less than 10%, this rule provides a structured approach to revising your investment amount upwards consistently.
The Impact of the 10% Hike Rule
Let’s understand the impact of this rule with an example:
- Without Hike:
- Monthly SIP: Rs 5,000
- Tenure: 30 years
- Annualised return: 12%
- Final Corpus: Rs 1.76 crore
- With 10% Annual Hike:
- Starting Monthly SIP: Rs 5,000
- SIP increase: 10% per year
- Tenure: 30 years
- Annualised return: 12%
- Final Corpus: Rs 4.42 crore
By simply increasing your SIP by 10% annually, you more than double the final corpus from Rs 1.76 crore to Rs 4.42 crore.
How to Implement the 10% Hike Rule
Implementing this rule is straightforward, especially with many investment platforms and apps offering the feature to modify SIP amounts easily. Here’s how to do it:
- Start with Your Current SIP: Begin with whatever amount is comfortable for you.
- Annual Review: Once a year, preferably at the start or when you get a salary hike, review your SIP amount.
- Increase SIP by 10%: Increase the monthly SIP amount by 10%. For example, if your current SIP is Rs 5,000, increase it to Rs 5,500.
- Modify Your SIP: Use your investment platform’s features to modify your existing SIP amount to the new figure.
Flexibility in the Hike Percentage
If a 10% hike seems challenging, you can opt for a lower percentage increase, like 5% or 3%. The key is to ensure that your investment contributions grow along with your income, even if it’s at a slower rate than 10%.
Benefits 10% Hike Rule
- Compounding Growth: Incremental increases in your investment contribute to the compounding effect, significantly boosting the final corpus.
- Adapts to Income Growth: It allows your investment to keep pace with your income growth, ensuring that your saving and investing habits evolve as you earn more.
- Mitigates Lifestyle Inflation: By allocating a portion of your income hikes to investments, you reduce the risk of increasing your spending proportionately with your income, a phenomenon known as lifestyle inflation.
The 10% Hike Rule is a powerful yet simple strategy for growing your investments over time. It leverages the potential of compounding returns and ensures that your investment contributions remain aligned with your financial growth, leading to a larger corpus in the long term. Whether you choose to increase your SIP by 10%, 5%, or even 3%, the critical aspect is to make regular increases a habit. This disciplined approach to investing can make a significant difference in achieving your financial goals.
⬇️You May Also Read ⬇️
➤7 Risk Management Techniques in Breakout and Retest Trading
➤Trade with Confidence: Mastering Breakout and Retest Concept in Trading
➤Mastering Breakout and retest trading strategy
➤Your Secret Weapon for Tax Savings: House Rent Allowance (HRA) and Other allowances
FAQ: Mastering Your Personal Finance Journey
What is the Net Worth Rule and how does it work?
The Net Worth Rule helps assess your financial well-being based on your age, income, and net worth. It involves calculating your total assets minus liabilities and comparing it to a target net worth based on your age and income.
What does the Rule of 70 indicate about inflation?
The Rule of 70 offers a quick method to estimate how fast the purchasing power of your money decreases due to inflation by dividing 70 by the current inflation rate.
What is the Net Worth Rule in personal finance?
The Net Worth Rule helps assess your financial health based on your age and pre-tax income by calculating your net worth (assets minus liabilities) and comparing it to a target net worth, adjusted for different countries.
How does the Rule of 72 assist in investment planning?
The Rule of 72 estimates the time it takes for an investment to double in value based on its annual rate of return, providing a quick way to gauge investment growth and compound interest effects.
What does the Rule of 70 indicate about inflation?
The Rule of 70 offers a quick method to estimate how fast the purchasing power of your money decreases due to inflation by dividing 70 by the current inflation rate.
How can the 100-Age Rule guide investment allocation?
The 100-Age Rule suggests allocating a percentage of your investment portfolio to equities based on the formula 100 minus your age, with the rest in less volatile debt investments, adjusting as you age.
What is the purpose of the 50-30-20 budgeting rule?
This rule is a budgeting guideline that suggests dividing your after-tax income into 50% for needs, 30% for wants, and 20% for savings and investments, aiming for balanced financial management.
How does the 6X Rule enhance financial security?
The 6X Rule advises saving an emergency fund worth six times your monthly expenses, providing a financial safety net for unexpected emergencies without dipping into investments.
What is the 20X Term Insurance rule?
It suggests having a term life insurance coverage that is at least 20 times your annual income to ensure sufficient financial security for your dependents in case of your untimely death.
How does the 25X Retirement Rule assist in retirement planning?
It suggests saving at least 25 times your annual expenses by retirement, based on the idea that you can safely withdraw 4% of your retirement fund annually without depleting it.
What is the 10% Hike Rule in investing?
The 10% Hike Rule recommends increasing your investment contributions, like SIPs in mutual funds, by 10% annually to match income growth and significantly boost potential returns.
What is the 25X Retirement Rule, and how is it used in financial planning?
The 25X Retirement Rule recommends having at least 25 times your annual expenses saved up by the time you retire to ensure your retirement savings are sufficient to support your lifestyle for many years.
How does the 40% EMI Rule help manage debt responsibly?
The 40% EMI Rule suggests that your total Equated Monthly Installments (EMIs) for all loans should not exceed 40% of your monthly income, ensuring a healthy balance between loan obligations and other financial priorities.
What is the 50-30-20 Rule, and how does it help in budgeting?
The 50-30-20 Rule recommends allocating 50% of your income to needs, 30% to desires, and 20% to investments, providing a simple guideline for effective budgeting.
