If you seriously wants to understand “Risk Management Techniques in Breakout and Retest Trading”.
You first have to understand Breakouts and Retests like:
- Defining Breakouts and Retests
- Characteristics of Breakout and Retest Patterns
- Identifying Breakout and Retest Opportunities
- Strategy to apply Breakout and Retest Trading
for this , Must Read this Two Post
- Trade with Confidence: Mastering Breakout and Retest Concept in Trading
- Mastering Breakout and retest trading strategy
Risk Management in Breakout and Retest Trading
Risk Management Fundamentals
Risk management is a crucial aspect of any trading or investment strategy. It involves understanding and mitigating the potential risks associated with financial activities to protect capital and ensure consistent returns. Here’s a detailed explanation of the fundamentals of risk management, including the concepts of risk vs reward, position sizing, setting stop losses, and the importance of risk-to-reward ratio:
- Risk vs Reward: Balancing the Equation:
- Risk and reward are two fundamental components of any financial decision. Risk refers to the potential for loss or uncertainty in achieving desired returns, while reward refers to the potential gain or profit.
- Balancing the risk and reward involves assessing the potential risks associated with an investment or trade against the potential rewards it offers. Traders and investors seek to maximize their rewards while minimizing their risks.
- Understanding the relationship between risk and reward is essential for making informed decisions. Higher potential rewards often come with higher levels of risk, and vice versa. Therefore, finding the right balance is key.
- Position Sizing: The Key to Consistent Trading:
- Position sizing refers to determining the appropriate amount of capital to allocate to a specific trade or investment. It involves considering factors such as account size, risk tolerance, and the probability of success.
- Proper position sizing helps traders manage risk by limiting the amount of capital exposed to any single trade. This reduces the impact of potential losses on overall portfolio performance.
- A commonly used method for position sizing is the percentage risk model, where traders risk a small percentage of their total capital on each trade. This ensures that losses are kept within manageable limits, even during periods of market volatility.
- Setting Stop Losses: Protecting Your Capital:
- A stop loss is a predefined price level at which a trader exits a losing position to limit losses. It acts as a safeguard against significant drawdowns and helps protect capital from excessive risk.
- Setting stop losses is a crucial aspect of risk management as it ensures that losses are controlled and do not spiral out of control. Traders should determine stop loss levels based on their risk tolerance and the volatility of the market.
- Stop losses can be set at various levels, including fixed monetary amounts, percentage of account balance, or based on technical indicators such as support and resistance levels.
- Importance of Risk-to-Reward Ratio:
- The risk-to-reward ratio is a metric used to assess the potential return of an investment relative to its risk. It is calculated by dividing the potential reward of a trade by its potential risk.
- A favorable risk-to-reward ratio indicates that the potential reward outweighs the potential risk, making the trade potentially profitable even if it doesn’t always win.
- Traders often aim for a risk-to-reward ratio of at least 1:2 or higher, meaning that for every dollar risked, there is a potential to make at least two dollars in profit. This ensures that winning trades can offset losses and contribute to overall profitability.
- By focusing on trades with favorable risk-to-reward ratios, traders can improve their consistency and long-term success while effectively managing risk.
In conclusion, risk management fundamentals are essential for traders and investors to navigate the financial markets successfully. By understanding and implementing concepts such as risk vs reward, position sizing, setting stop losses, and assessing risk-to-reward ratios, individuals can protect their capital, minimize losses, and achieve consistent returns over time.
Techniques for Managing Risk in Breakout Trading
Breakout trading is a popular strategy used by traders to capitalize on significant price movements that occur when an asset’s price breaks through a predetermined support or resistance level. However, like any trading strategy, breakout trading involves inherent risks. Effective risk management techniques are crucial to mitigate these risks and enhance the probability of successful trades. Below, I’ll explain in detail various techniques for managing risk in breakout trading:
- Assessing Market Volatility
- Utilizing Support and Resistance Levels
- Confirmation Signals: Filtering False Breakouts
- Setting Proper Position Sizes
- Using Stop Loss Orders Effectively
- ATR (Average True Range) Strategy
- Scaling In and Scaling Out of Trades
1. Assessing Market Volatility
Managing risk in breakout trading requires a solid understanding of market volatility. Volatility refers to the degree of variation of a trading price series over time, and it can greatly impact the effectiveness of your trading strategies, especially when it comes to breakouts.
Market volatility plays a significant role in breakout trading. Higher volatility often leads to more frequent and substantial breakouts, but it also increases the risk of false breakouts. Traders can assess volatility using indicators like the Average True Range (ATR), Bollinger Bands, or historical price data. Understanding volatility helps traders adjust their strategies and risk parameters accordingly.
Breakout Trading and Volatility
A breakout occurs when the price of an asset moves outside a defined support or resistance level with increased volume. These levels are typically identified through historical price patterns. Breakouts can signal the start of a new trend or a significant move in the direction of the breakout, offering traders potential opportunities for profit.
However, the relationship between market volatility and breakout trading is double-edged. On one hand, higher volatility can increase the number of trading opportunities due to more frequent and substantial price movements. On the other hand, it can also lead to a higher risk of false breakouts—situations where the price breaks past a certain level but then quickly reverses direction, often leading to losses.
Assessing Market Volatility
To navigate this volatile landscape, traders can employ various indicators and techniques to assess market volatility:
Average True Range (ATR)
The ATR indicator measures market volatility by decomposing the entire range of an asset price for that period. Specifically, it calculates the average of true ranges over a specified number of periods. A higher ATR value indicates higher volatility, suggesting that breakouts might be more pronounced but could also be riskier. Traders can use ATR to adjust their stop-loss orders and take-profit points to match the current market volatility.
Bollinger Bands
Bollinger Bands are another tool traders can use to assess volatility. These bands adjust themselves based on market volatility, widening during volatile periods and contracting during calmer periods. A breakout from a Bollinger Band could indicate a potential trading opportunity. However, traders should be cautious and look for additional confirmation to avoid false breakouts.
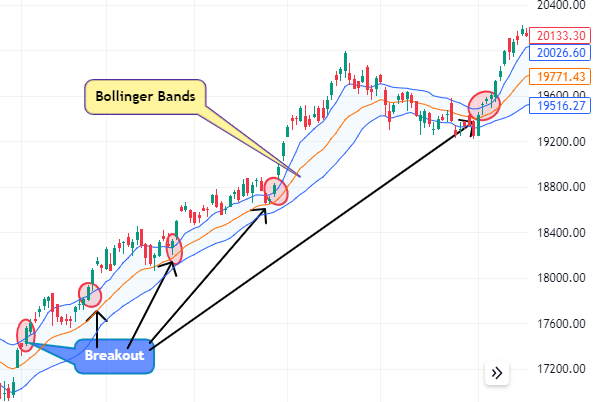
Historical Price Data
Analyzing historical price data can also provide insights into the volatility patterns of a particular asset. Traders can look for patterns in how the asset’s price reacted in different volatility conditions in the past to inform their current trading decisions.
Adjusting Strategies Based on Volatility
Understanding volatility is crucial for adjusting trading strategies and risk parameters. For instance, in high volatility conditions, traders might choose to:
- Widen their stop-loss orders to allow for more price movement before exiting a trade.
- Decrease the size of their positions to reduce potential losses.
- Look for higher risk-to-reward ratios to compensate for the increased risk of false breakouts.
Conversely, in lower volatility conditions, traders might tighten their stop losses or increase their position sizes, given the lower expected price movement.
Assessing market volatility is a fundamental aspect of managing risk in breakout trading. By understanding and adapting to the current volatility environment, traders can make more informed decisions, adjusting their strategies to either capitalize on the opportunities presented by high volatility or protect themselves against its risks. Incorporating volatility assessment into your trading routine can help you navigate the complex and ever-changing landscape of the financial markets with greater confidence and success.
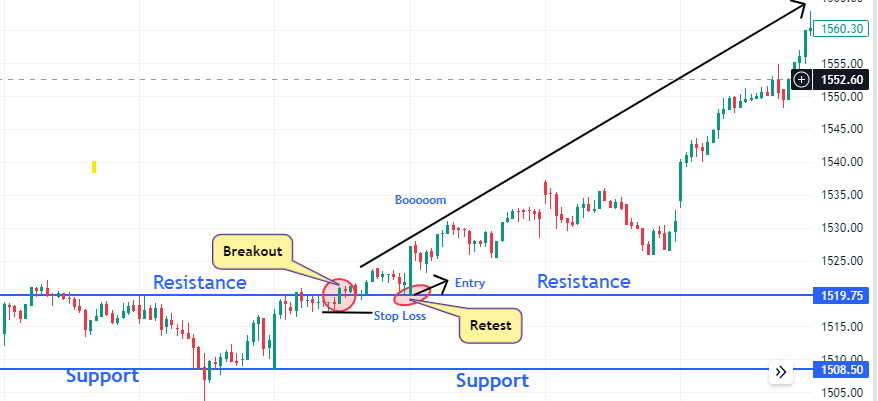
2. Utilizing Support and Resistance Levels:
Managing risk in breakout trading by utilizing support and resistance levels involves several steps to identify potential trading opportunities while minimizing the risk of false breakouts. Here’s a steps to Follow:
- Identify Key Support and Resistance Levels: Begin by examining historical price data to identify significant support and resistance levels. These levels are typically formed at points where the price has previously struggled to move beyond. Look for areas where the price has bounced off multiple times, indicating strong support or resistance.
- Confirm Validity of Support and Resistance Levels: Once you’ve identified potential support and resistance levels, confirm their validity by observing how the price reacts when it approaches these levels. A valid support level should see the price bounce back up when tested, while a valid resistance level should see the price retreat when approached.
- Wait for Breakout Confirmation: When the price approaches a resistance level in an uptrend or a support level in a downtrend, wait for a breakout confirmation before entering a trade. Breakout confirmation occurs when the price convincingly breaches the support or resistance level, indicating a potential trend continuation.
- Set Entry and Exit Points: Once a breakout is confirmed, set your entry point slightly above the breakout level for a long trade or slightly below for a short trade. This helps ensure that you enter the trade after the breakout has occurred, reducing the risk of false breakouts.
- Place Stop Loss Orders: To manage risk effectively, place stop-loss orders just below the breakout level for long trades and just above for short trades. This helps limit potential losses if the breakout fails and the price reverses direction.
- Consider Risk-Reward Ratio: Before entering a trade, assess the risk-reward ratio to ensure that the potential reward outweighs the risk. Aim for a favorable risk-reward ratio, such as 1:2 or higher, to justify the trade.
- Monitor Trade Progress: Once you’ve entered a trade, monitor its progress closely. Pay attention to how the price behaves around support and resistance levels, as well as any signs of trend continuation or reversal.
- Adjust Stop Loss Orders: As the trade progresses in your favor, consider adjusting your stop-loss orders to lock in profits and protect your capital. This can involve trailing your stop-loss orders behind the price to secure gains while allowing for potential further upside. You can just shift your SL below every Swing in Uptrend or above every Swing in downtrend or shift your SL as Moving Average move.
- Exit the Trade Appropriately: Finally, exit the trade when the price reaches your predefined target or shows signs of a trend reversal. Avoid being greedy and stick to your trading plan to ensure consistent risk management.
By following these steps and utilizing support and resistance levels effectively, you can manage risk in breakout trading while maximizing your potential for profits. Remember to always trade with discipline and adhere to your risk management strategy to achieve long-term success in trading.
3. Confirmation Signals: Filtering False Breakouts
Managing risk in breakout trading, particularly when it comes to avoiding false breakouts, is a crucial skill that traders need to develop. False breakouts can lead to unnecessary losses, as they trick traders into believing that the price will continue in the direction of the breakout, only for it to reverse. Here’s how traders can use confirmation signals to filter out false breakouts and enhance their risk management strategy:
Increased Trading Volume
One of the primary confirmation signals that traders use to identify genuine breakouts is increased trading volume. A significant increase in volume suggests strong market interest and lends credibility to the breakout. If the price breaches a support or resistance level with substantial volume, it indicates that many traders are supporting the price move, making it less likely to be a false breakout.
Candlestick Patterns
Candlestick patterns are another effective tool for confirming breakouts and Retest Trading. Certain patterns can provide insights into market sentiment and potential price movements.
For example:
Engulfing Patterns:
- A bullish engulfing pattern occurs when a large green candle follows a small red candle, completely engulfing it. if This pattern formed at a retesting resistance level suggests a strong buying pressure and a potential genuine breakout.
- A Bearish engulfing pattern occurs when a large Red candle follows a small Green candle, completely engulfing it. if This pattern formed at a retesting Support level suggests a strong Selling pressure and a potential genuine breakout.
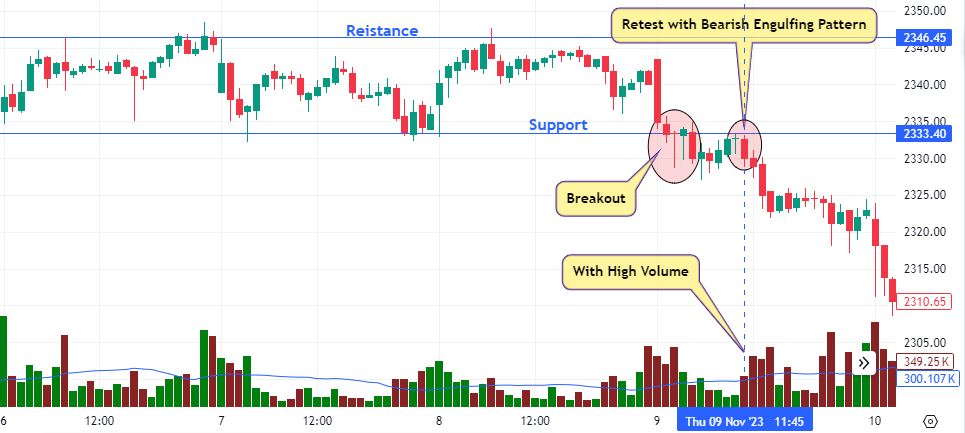
- Hammer or Doji: These patterns indicate indecision in the market but, when occurring in the context of a breakout with other confirmatory signals, can suggest a reversal or continuation. A hammer pattern near support or a doji at resistance, followed by a breakout, can be a good confirmation of the breakout’s validity.
Technical Indicators
Additional technical indicators like the MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence) or RSI (Relative Strength Index) can also provide confirmation signals.
- MACD: A momentum indicator that shows the relationship between two moving averages of an asset’s price. A crossover of the MACD line above the signal line can be a bullish signal, especially if it occurs in conjunction with a breakout above resistance.
- RSI: A momentum oscillator that measures the speed and change of price movements. An RSI level above 70 is considered overbought, while below 30 is considered oversold. For breakout trading, an RSI moving out of these extremes can confirm momentum in the direction of the breakout.
The Waiting Game
One of the simplest yet effective risk management techniques is patience. Waiting for these confirmation signals before entering a trade can help traders avoid the pitfalls of false breakouts. It’s important to remember that not all breakouts will be accompanied by clear confirmation signals, and in some cases, waiting might mean missing out on potential opportunities. However, the primary goal of using confirmation signals is to reduce risk and increase the likelihood of entering trades with a higher probability of success.
So, by incorporating increased trading volume, specific candlestick patterns, and additional technical indicators as part of their strategy, traders can significantly enhance their ability to filter out false breakouts. This approach helps in managing risk more effectively, preserving capital, and increasing the chances of successful trades in breakout trading.
4. Setting Proper Position Sizes
Managing risk in breakout trading through proper position sizing is an essential strategy for safeguarding your capital while pursuing potential profits. This strategy hinges on determining the optimal amount of capital to allocate to each trade, taking into account your total trading capital, your tolerance for risk, and specific trade characteristics such as the distance to your stop-loss level. Here’s a step-by-step guide to implementing this strategy:
Understand Your Risk Tolerance
Before you calculate your position size, you need to assess your risk tolerance. This is a personal measure and varies from trader to trader. Some traders might be comfortable risking 2% of their trading capital on a single trade, while others might prefer a more conservative approach, like 1% or even less.
Calculate Position Size
- Use the 1% or 2% Rule: A common guideline is to risk only 1% to 2% of your total trading capital on any given trade. This means if the trade doesn’t go your way, you’re only risking a small portion of your capital.
- Account Size Calculation: Determine your account size and apply the 1% or 2% rule. For example, if your trading account is $20,000 and you’re using the 2% rule, you’re willing to risk up to $400 on a single trade.
- Determine Stop-Loss Level: The stop-loss level is crucial in this calculation. It’s the price level at which your trade will be automatically closed to prevent further losses. The distance between your entry point and your stop-loss level, along with your account size and risk level, will guide your position size.
- Calculate Position Size: The formula for position size is (Account Risk / Trade Risk) = Position size. Here, account risk is the dollar amount you’re willing to risk (based on the 1% or 2% rule), and trade risk is the difference between the entry point and the stop-loss level in dollars. This calculation ensures you’re risking only the predetermined amount on the trade, regardless of where the stop-loss is set.
Implement the Strategy
- Adapt to Market Conditions: It’s important to adjust your position size based on changing market conditions or fluctuations in your trading account size. If your account grows, so does the dollar amount risked per trade (still adhering to the 1% or 2% rule). Conversely, if your account size decreases, the amount risked per trade should decrease accordingly.
- Preserve Capital: The primary goal of proper position sizing is to preserve capital during downturns. By limiting how much is risked on each trade, you ensure that no single trade significantly impacts your overall capital, allowing you to stay in the game even after a series of losses.
Review and Adjust
- Regular Review: Regularly review your risk management strategy to ensure it aligns with your current financial situation and trading goals. Adjust your risk tolerance and position sizing as needed.
Proper position sizing is a cornerstone of risk management in breakout trading. By adhering to a disciplined approach, based on your risk tolerance and market conditions, you can limit potential losses, preserve capital, and position yourself for long-term trading success.
5. Using Stop Loss Orders Effectively:
Managing risk in breakout trading with the effective use of stop-loss orders is a fundamental strategy to safeguard your investments. These orders serve as a safety net, ensuring that losses do not spiral out of control if the market moves unfavorably. Here’s a detailed guide on how to manage risk by using stop-loss orders effectively in breakout trading:
1. Understanding Stop-Loss Orders
A stop-loss order is an automatic order placed with your broker to sell a security when it reaches a certain price. For long positions, the stop-loss order is set below the current market price, while for short positions, it is set above. This tool is designed to limit an investor’s loss on a security position.
2. Setting Strategic Stop-Loss Levels
- Below Support for Long Positions: When entering a long position on a breakout, place your stop-loss just below a significant support level. The idea is that if the price falls back below this level, the breakout might not be sustainable, and it’s a signal to exit the trade to avoid further losses.
- Above Resistance for Short Positions: Conversely, when taking a short position after a downward breakout, set the stop-loss order just above a key resistance level. A move above this level could indicate the market is reversing in favor of an upward trend, suggesting it’s time to cut losses.
3. Account for Market Volatility
- Volatility-Adjusted Stop-Losses: The placement of your stop-loss should take into account the asset’s volatility. Highly volatile markets might require setting wider stop-losses to avoid being stopped out by normal price fluctuations. Conversely, in less volatile markets, stop-loss orders can be set tighter to protect profits and minimize losses.
4. Consider Market Conditions
- Market Conditions and Slippage: Be aware that during periods of high volatility or when trading less liquid assets, stop-loss orders might not be executed at the exact predetermined level due to slippage. To mitigate this, traders might use stop-limit orders instead of stop-market orders, though this comes with the risk of the order not being executed at all if the price moves too quickly.
5. Continuous Evaluation and Adjustment
- Regular Review: It’s crucial to regularly review and, if necessary, adjust your stop-loss orders based on changes in market dynamics or new patterns in support and resistance levels. As a trade moves in your favor, consider using a trailing stop-loss to lock in profits while still giving the trade room to grow.
Effectively using stop-loss orders in breakout trading is about more than just setting a safety net; it’s about strategic planning and ongoing adjustment to market conditions. By placing stop-loss orders thoughtfully, taking into account support and resistance levels, and adjusting for volatility and market conditions, traders can better manage risk and protect their investments from significant losses.
6. ATR (Average True Range) Strategy:
Using the Average True Range (ATR) strategy is a dynamic approach to managing risk in breakout trading. This method helps traders adapt their strategies according to the market’s volatility, ensuring that risk management practices are aligned with current market conditions. Here’s how you can effectively utilize the ATR strategy to manage risk in breakout trading:
Understanding the ATR Indicator
The ATR indicator measures the market’s volatility by calculating the average range between the high and low prices of an asset over a given period. This gives traders a quantitative measure of how much the price of an asset typically moves, helping them to anticipate potential price movements.
Setting Stop-Loss Orders with ATR
One of the primary ways to use ATR in managing risk is by setting stop-loss orders. A stop-loss order is a predetermined price level at which your trade will be automatically closed to prevent further losses. By using ATR to inform your stop-loss levels, you can adjust them according to the market’s volatility:
- For High Volatility: A higher ATR indicates that the asset’s price is making larger movements. In such scenarios, it’s wise to set wider stop-loss orders to avoid getting stopped out by normal market fluctuations. This gives your trade more room to breathe and aligns the risk management with the current market conditions.
- For Low Volatility: A lower ATR suggests that the asset’s price movements are smaller. Here, you can afford to set tighter stop-loss orders, as the risk of wide price fluctuations is reduced. This helps in protecting your capital while ensuring that you’re not unnecessarily exposed to market movements.
Example:
Let’s say you’re trading a stock that has broken out above a resistance level, signaling a potential buy opportunity. You check the ATR and find it’s 10 Rupees. This means, on average, the stock’s price moves about 10 Rupees per day.
- High Volatility Scenario: If recent market conditions suggest increasing volatility, you might decide to set your stop-loss at 1.5 ATR below your entry point. If you entered the trade at ₹1000, your stop-loss would be at₹985 (₹1000 – (1.5 * ₹10)).
- Low Volatility Scenario: In a period of lower volatility, you might set your stop-loss at just 1 ATR below your entry point. Using the same entry price of ₹1000, your stop-loss would now be at ₹990 (₹1000 – (1 * ₹10)).
Adjusting Position Sizes
Another aspect of managing risk with the ATR strategy involves adjusting position sizes based on the volatility. The idea is to balance the risk by altering how much capital you’re allocating to a trade:
- Higher Volatility (Higher ATR): With the risk of larger price movements, it’s prudent to reduce your position size. This way, even if the market moves against your position, the impact on your trading capital is minimized.
- Lower Volatility (Lower ATR): In periods of lower volatility, you might choose to increase your position size since the risk of drastic price movements is lower. This allows you to capitalize on potential gains without disproportionately increasing your risk exposure.
Example:
Assuming you have a rule to risk only ₹200 per trade:
- High Volatility Scenario: With an ATR of 10 Rupees and deciding on a stop-loss set at 1.5 ATR (15 Rupees away), you would calculate your position size to ensure you’re not risking more than ₹200. Thus, you could buy up to 13 shares (₹200 / ₹15 per share).
- Low Volatility Scenario: If the ATR is 5 Rupees, allowing for a tighter stop-loss at 1 ATR (₹10), you could afford to buy more shares while still risking only ₹200. In this case, your position size could be up to 20 shares (₹200 / ₹10 per share).
Thus, by using the ATR strategy, the trader can effectively manage risk by adjusting stop-loss levels and position sizes based on market volatility, thereby increasing the probability of successful breakout trades while minimizing potential losses.
How to Implementing the ATR Strategy
- Calculate the ATR for the asset you’re interested in trading, using a time period that aligns with your trading strategy.
- Determine Stop-Loss Levels based on the current ATR value, adjusting for the asset’s volatility.
- Adjust Position Sizes in accordance with the ATR, ensuring that you’re managing risk appropriately for the market’s current conditions.
By integrating the ATR strategy into your breakout trading approach, you can tailor your risk management practices to the ever-changing market volatility, protecting your capital while positioning yourself to capitalize on breakout opportunities.
7. Scaling In and Scaling Out of Trades
Managing risk in breakout trading through the strategies of scaling in and scaling out of trades is a methodical approach that can significantly enhance the efficiency of your trading and the management of your risk exposure. Let’s dive deeper into how you can implement these strategies effectively:
Scaling In: Gradually Increasing Your Position
- Start Small: When you identify a potential breakout, instead of committing a large portion of your capital at once, start with a small position. This initial entry should be based on your risk management rules, such as a certain percentage of your trading capital or a fixed monetary amount you’re willing to risk.
- Add to the Position: As the price moves in the desired direction and the breakout is confirmed, you can gradually increase your position. This could be done at predetermined price levels or after the market has met specific technical conditions that reinforce the strength of the trend.
- Use Tight Stop Losses for New Entries: For each additional entry, place tight stop losses to protect the new positions. This ensures that if the market reverses, the impact on your overall position is minimized.
Scaling Out: Locking in Profits
- Partial Profits: As the trade progresses favorably, begin to scale out of the position by taking partial profits. This could be done at specific price targets, percentage gains, or after the price reaches significant resistance levels.
- Adjust Stop Losses: After securing part of your profits, move the stop losses for the remaining position to break-even or to a position where profits are locked in. This strategy reduces the risk of a successful trade turning into a losing one.
- Flexible Exit Strategy: Keep a portion of your trade running as long as the trend remains strong. This allows you to capitalize on extended price movements. However, be ready to exit this remaining position if the market shows signs of reversal or if key support levels are broken.
Benefits of Scaling In and Out
- Risk Management: By not committing all your capital at once, you reduce the risk associated with sudden market reversals. Scaling out allows you to lock in profits, ensuring that you secure a return on your investment even if the market turns against you.
- Mitigating Market Fluctuations: This approach smooths out the impact of price volatility since you’re not entering or exiting your entire position at a single price point. It offers flexibility in handling market fluctuations.
- Minimizing Emotional Trading: Scaling in and out requires a disciplined approach and predefined criteria for adjusting your position size. This helps to minimize emotional decisions, making your trading more systematic and less susceptible to fear or greed.
Implementing scaling in and scaling out strategies in breakout trading not only helps in managing risk but also in enhancing the potential for profitability by allowing traders to adapt to market conditions dynamically.
The Importance of Patience and Discipline in Risk Management
The essence of successful breakout trading lies not just in the strategies and techniques employed but significantly in the trader’s mindset, particularly in their patience and discipline. These virtues are indispensable in managing risk and ensuring long-term success in the volatile world of trading.
The mantra of patience and discipline is not just philosophical advice but a strategic cornerstone in the world of breakout trading. The markets are unpredictable, often tempting traders to make hasty decisions. However, the essence of successful risk management in breakout trading lies in the ability to stay patient and disciplined. Here’s a deeper look into why these virtues are indispensable:
Patience: The Art of Waiting for the Right Moment
In breakout trading, not every signal is worth acting upon. The markets can present numerous false breakouts or setups that don’t fully meet your trading criteria. Patience is about waiting for those high-probability setups that align with your trading plan. This means letting go of the fear of missing out (FOMO) and resisting the urge to jump into trades prematurely.
Patience also plays a critical role when waiting for confirmations of a breakout. Instead of entering a trade immediately after the price breaches a support or resistance level, a patient trader waits for additional confirmation (like a closing candlestick outside the breakout level or wait for a Retest the same breakout level ) to increase the chances of a successful trade.
- Waiting for High-Probability Setups: Breakout trading is all about capitalizing on moments when the price breaks beyond a predefined resistance or support level. However, not all breakouts are created equal. Patience allows traders to wait for setups that have a higher probability of success, which are often characterized by strong market signals and confluence factors that support the breakout move.
- Avoiding Overtrading: A common pitfall for many traders is the urge to trade constantly, often driven by the fear of missing out (FOMO). Patience helps in curbing this impulse, ensuring that traders only engage when the conditions align perfectly with their trading plan, thus minimizing exposure to unnecessary risk.
Discipline: Sticking to Your Trading and Risk Management Plan
Discipline is the complementary counterpart to patience. While patience is about waiting for the right opportunity, discipline is about what you do once the opportunity presents itself. This includes sticking to pre-defined entry and exit points, position sizing, and stop-loss orders, regardless of how the market appears to be moving post-entry.
Emotions, particularly fear and greed, can derail even the most experienced traders. Discipline ensures that you’re not swayed by these emotions. For instance, greed may tempt you to hold onto a position longer than your trading plan dictates in the hope of squeezing out more profit, potentially resulting in a loss if the market reverses. Similarly, fear may prompt you to exit a trade too early, leaving money on the table. Discipline ensures that you follow your trading plan to the letter, making decisions based on logic and strategy rather than emotion.
The volatile nature of markets can trigger emotional responses such as fear, greed, or frustration. Patience and discipline together form a buffer against these emotions, enabling traders to maintain a clear head and make rational decisions. By exercising patience, traders learn to wait out the noise and focus on substantial market moves. Discipline, in turn, helps in sticking to a trading plan that is designed to navigate through market volatility effectively.
Maintaining a Rational Approach
Together, patience and discipline foster a rational and systematic approach to trading. This rationality is key in managing risk effectively. It helps traders to maintain control over their trading decisions, ensuring that each trade is executed based on a clear analysis and understanding of the market, rather than impulsive reactions to market noise.
In summary, breakout trading offers lucrative opportunities for profit, but it also involves inherent risks. Effective risk management techniques, including assessing market volatility, utilizing support and resistance levels, confirming breakouts, employing the ATR strategy, setting proper position sizes, using stop-loss orders, scaling in and out of trades, and maintaining patience and discipline, are essential for mitigating risks and maximizing the probability of success in breakout trading.
⬇️You May Also Read ⬇️
➤Trade with Confidence: Mastering Breakout and Retest Concept in Trading
➤Mastering Breakout and retest trading strategy
➤Your Secret Weapon for Tax Savings: House Rent Allowance (HRA) and Other allowances
➤Mastering Income Tax savings: A Beginner’s Guide to Save Money Legally
➤Top 10 Powerful Reasons to Invest in Mutual Funds
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Risk Management in Breakout and Retest Trading
What is risk management in trading?
Risk management in trading refers to the process of identifying, analyzing, and taking steps to minimize or control exposure to financial risk. It involves strategies to protect capital and ensure consistent returns, including balancing risk vs reward, proper position sizing, setting stop losses, and understanding the risk-to-reward ratio.
Why is the risk-to-reward ratio important in breakout trading?
The risk-to-reward ratio is crucial because it helps traders assess the potential return of an investment relative to its risk. A favorable risk-to-reward ratio means the potential rewards outweigh the risks, making a trade worthwhile. It ensures that even with some losses, the winning trades can offset them, contributing to overall profitability.
How does position sizing affect risk management in breakout trading?
Position sizing is key to managing risk as it determines the amount of capital to allocate to a specific trade, considering factors like account size and risk tolerance. Proper position sizing helps limit exposure on a single trade, reducing the impact of potential losses on the overall portfolio, thus enabling consistent trading.
What is the role of stop losses in breakout trading?
Stop losses act as a safeguard against significant drawdowns by automatically closing a trade at a predefined price level to limit losses. They are essential for controlling losses and protecting capital from excessive risk, making them a cornerstone of risk management in breakout trading.
Can assessing market volatility improve risk management in breakout trading?
Yes, understanding market volatility is vital as it influences the frequency and magnitude of breakouts. Assessing volatility helps traders adjust their strategies and risk parameters, like widening stop losses during high volatility, to better manage the risk of false breakouts and enhance trade success.
What are some techniques for managing risk in breakout trading?
Techniques include assessing market volatility, utilizing support and resistance levels for entry/exit points, using confirmation signals to filter false breakouts, employing the ATR (Average True Range) strategy to adjust stop losses and position sizes according to volatility, and scaling in and out of trades to manage exposure.
How can traders use support and resistance levels to manage risk?
Traders can identify potential breakout opportunities and set strategic entry and exit points by analyzing key support (price floor) and resistance (price ceiling) levels. Placing stop losses just below or above these levels, respectively, helps limit potential losses if the market reverses after a breakout.
What is the significance of patience and discipline in risk management?
Patience allows traders to wait for high-probability setups, avoiding overtrading and impulsive decisions. Discipline ensures adherence to a trading plan, maintaining a systematic approach to managing risk, which is essential for long-term success in breakout trading.
How does the ATR strategy help in managing risk?
The Average True Range (ATR) strategy uses volatility measures to adjust stop-loss orders and position sizes, ensuring they are aligned with current market conditions. It helps manage the risk of sudden market moves by adapting trading strategies to the level of volatility.
Why is scaling in and out of trades considered a risk management technique?
Scaling in (gradually increasing a position) and scaling out (taking partial profits) allows traders to manage their exposure to the market dynamically. It helps in minimizing risks associated with sudden market reversals and locking in profits, ensuring that traders can capitalize on profitable moves without risking their entire position.

2 thoughts on “7 Risk Management Techniques in Breakout and Retest Trading”